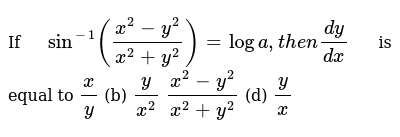
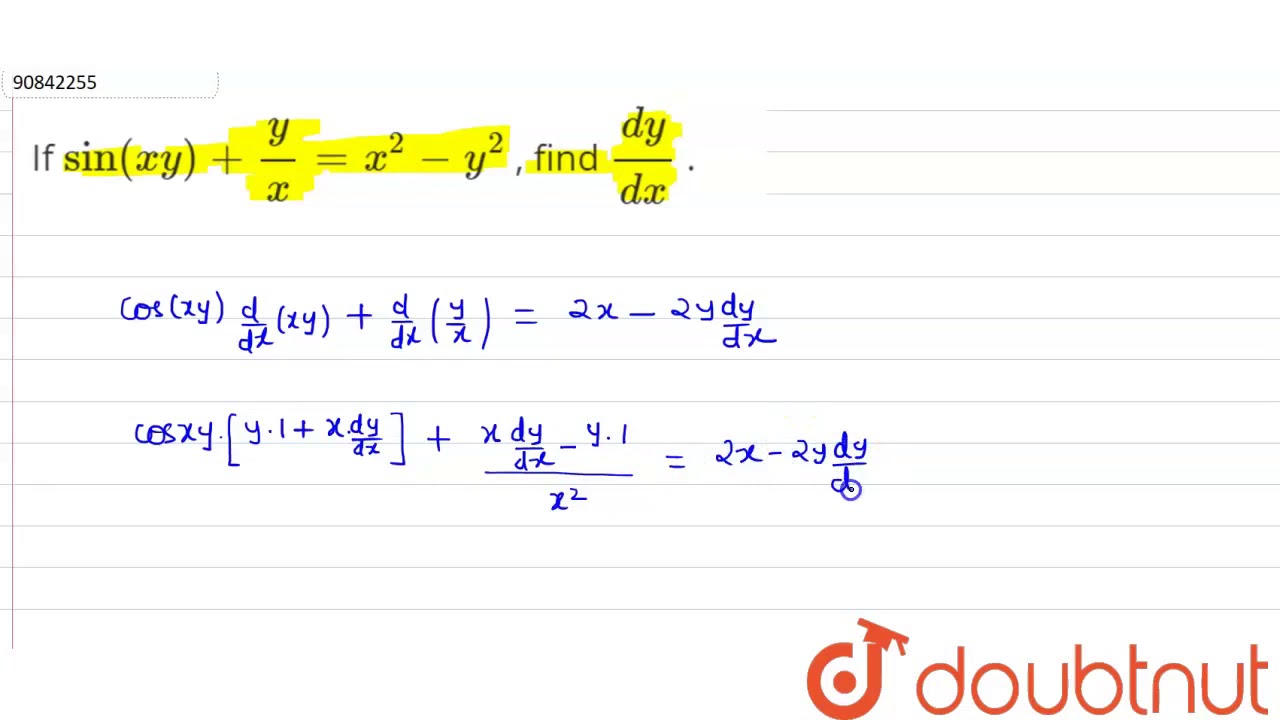
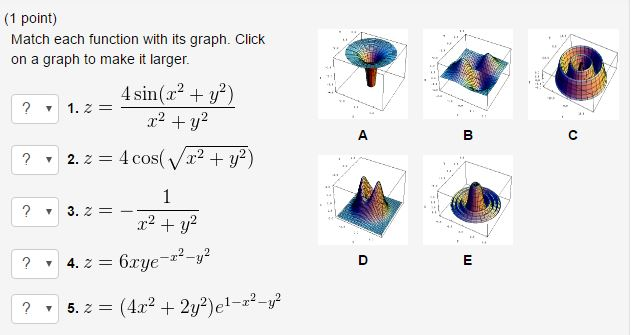
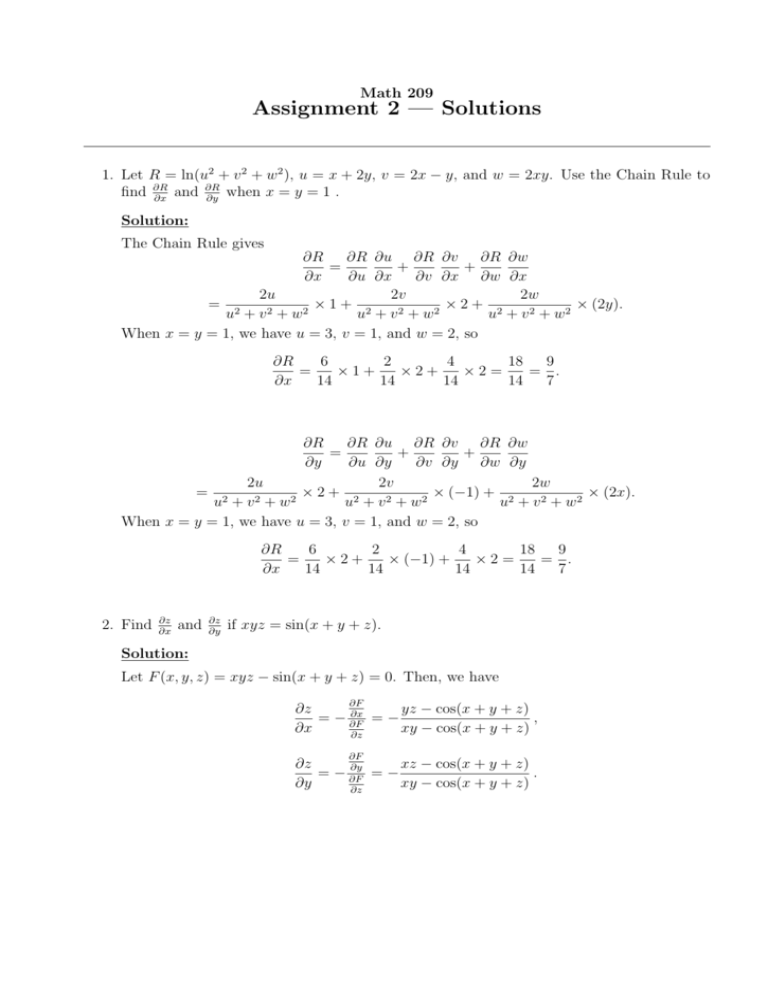
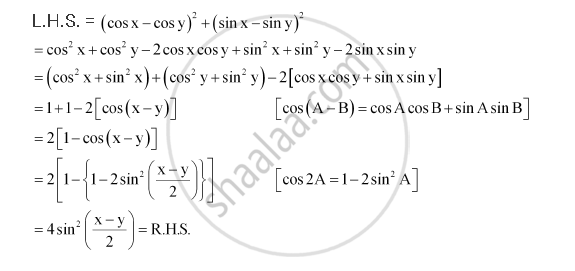
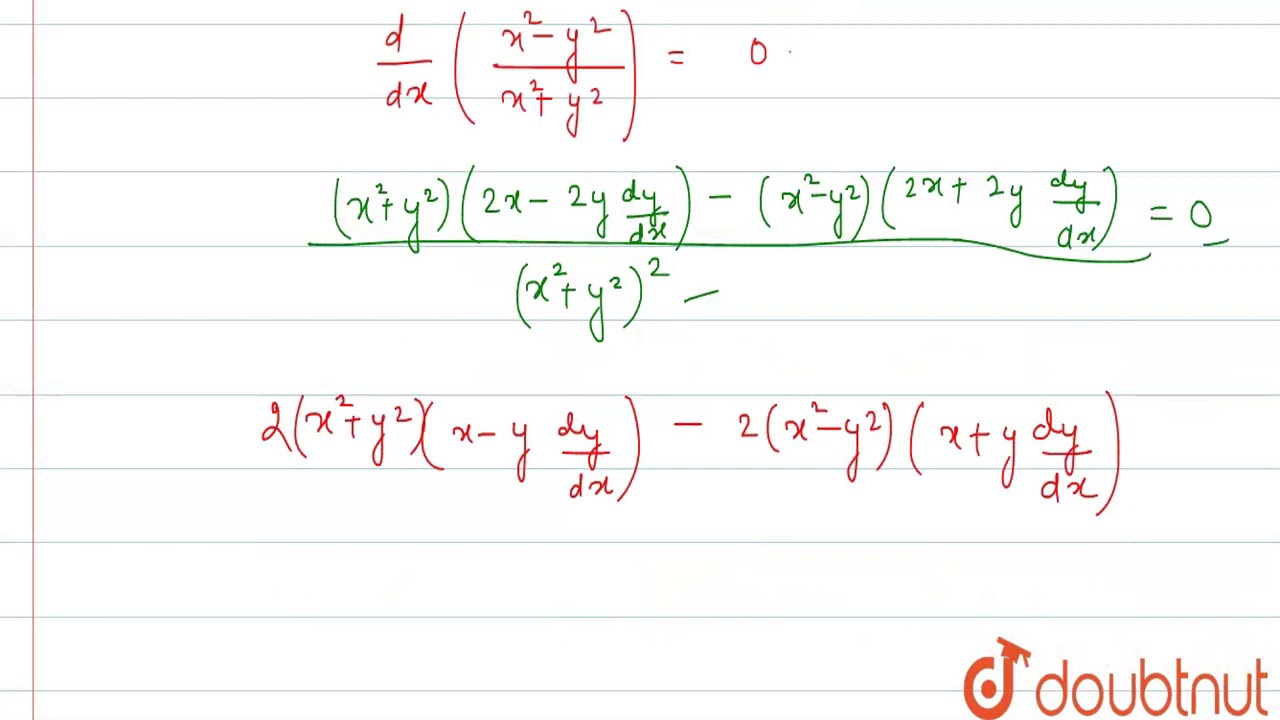
If Sin 1 X 2 Y 2 X 2 Y 2 Loga T H E N Dy Dx Is Equal To X Y B Y X 2 X 2 Y 2 X 2 Y 2 D Y X
ˇ arcsin(x p 1 y2 y 1 x2);Y' = 8)Find dy / dx by implicit differentiation 4 x2 3 xy − y2 = 2 y' = 9)Use implicit differentiation to find an equation of the tangent line to the curve at the given point x2 2 xy − y2 x = 51, (5, 7) (hyperbola) y = 10)Find the exact value of each expression, if it is defined
(x^2+y^2)*sin(1/sqrt(x^2+y^2))
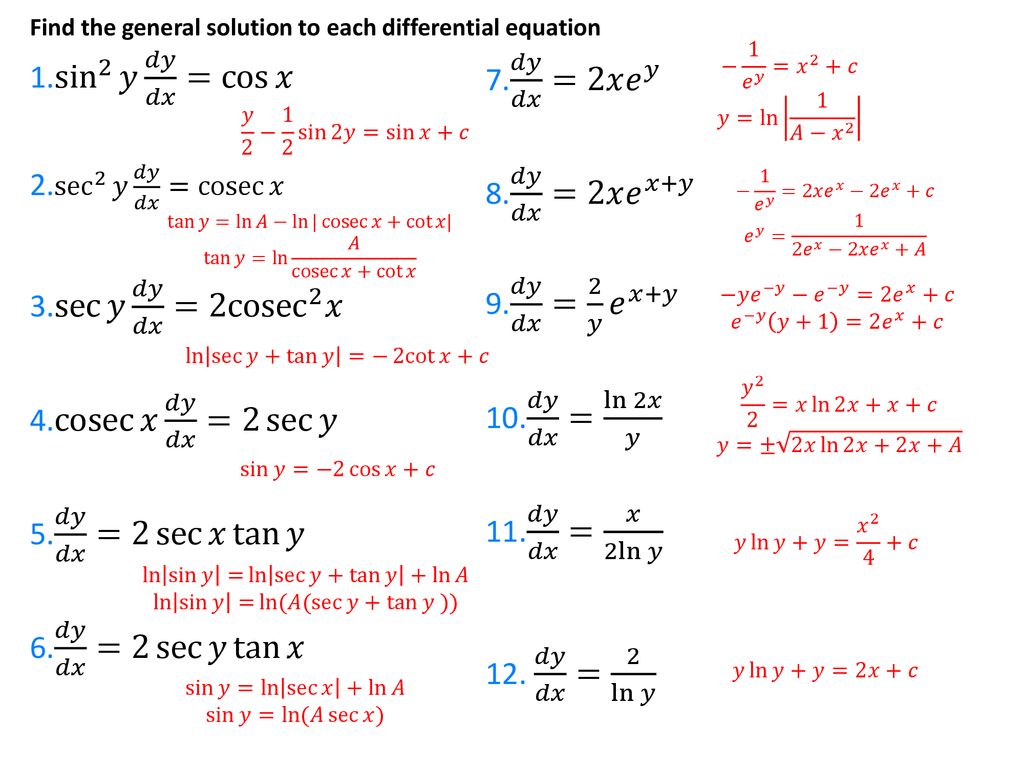
(x^2+y^2)*sin(1/sqrt(x^2+y^2))-∂x = y2 x2 y2 1 y = y x2 y2 = ∂v ∂y (1) − ∂u ∂y = − y2 x 2y −x y 2 = x x2 y = ∂v ∂x (2) By (1), v = 1 2 log(x2 y2)C(x), and by (2) ∂v ∂x = x x 2y C′(x) = x x y2 so C′(x) = 0andC(x) is a constant, call it D Therefore, v(x,y) = 1 2 log(x2 y2)D Question 3 (p86 #13) Show, if u(x,y) and v(x,y) are ∴ y c = C 1 cos x C 2 sin x (1) y = A cos x B sin x (2) be the complete solution of the given equation where A and B are to be found The general solution is y = Ay 1 By 2 We have y 1 = cos x and y 2 = sin x y′ 1 = – sin x and y′ 2 = cos x W = y 1 y' 2 y 2 y' 1 = cos x cos x sin x sin x = cos 2 x sin 2 x = 1
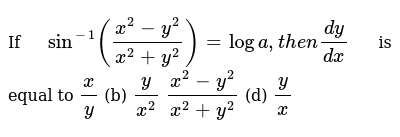
If Sin 1 X 2 Y 2 X 2 Y 2 Loga T H E N Dy Dx Is Equal To X Y B Y X 2 X 2 Y 2 X 2 Y 2 D Y X
Ex , 3 Find the area of the region bounded by the curves 𝑦=𝑥22, 𝑦=𝑥, 𝑥=0 and 𝑥=3 Here, 𝑦=𝑥22 𝑦−2=𝑥^2 𝑥^2=(𝑦−2) So, it is a parabola And, 𝑥=𝑦 is a line x = 3 is a line x = 0 is the yaxis Finding point of intersection B & C Point B Point B is intersection2 The number of 4 digit numbers without repetition that can be formed using the digits 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 in which each number has two odd digits and two even digits isF (x,y)=x^2y^2 WolframAlpha Volume of a cylinder?
TRIGONOMETRY LAWS AND IDENTITIES DEFINITIONS sin(x)= Opposite Hypotenuse cos(x)= Adjacent Hypotenuse tan(x)= Opposite Adjacent csc(x)=2ˇ arccos(xy q (1 x2)(1 y2));Fy = −sin(x2 y), fyx = −cos(x2 y)2x d) both sides are f0 (x)g 0 (y) 2 (fx)y = ax6y, (fy)x = 2x6y;
(x^2+y^2)*sin(1/sqrt(x^2+y^2))のギャラリー
各画像をクリックすると、ダウンロードまたは拡大表示できます
 |  | |
 |  | |
 |  | |
「(x^2+y^2)*sin(1/sqrt(x^2+y^2))」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 | 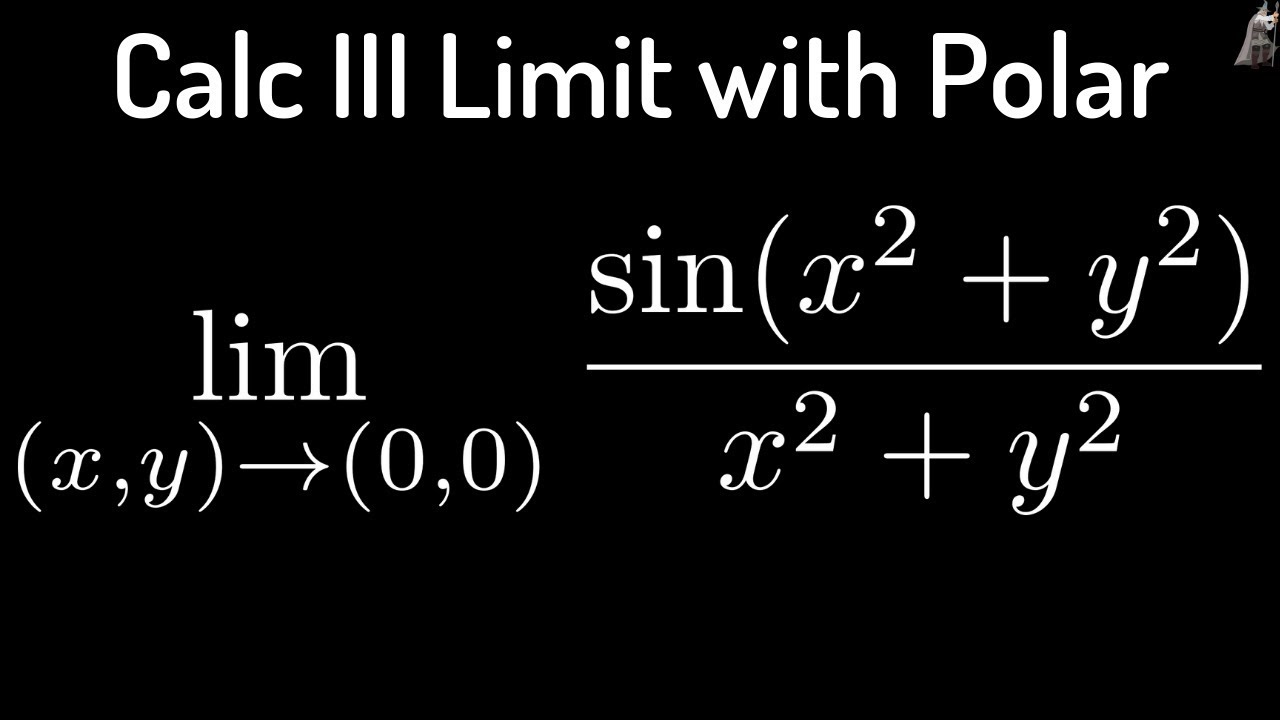 | |
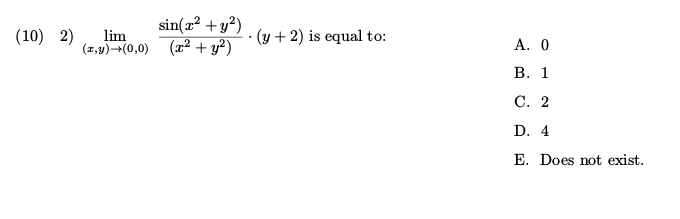 |  |  |
 |  | |
「(x^2+y^2)*sin(1/sqrt(x^2+y^2))」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | 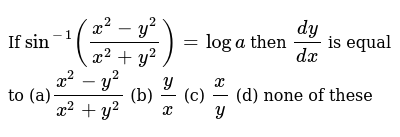 |
 |  |  |
 |  | |
「(x^2+y^2)*sin(1/sqrt(x^2+y^2))」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  | |
「(x^2+y^2)*sin(1/sqrt(x^2+y^2))」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
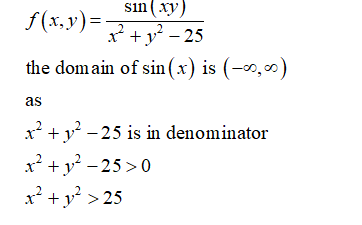 | 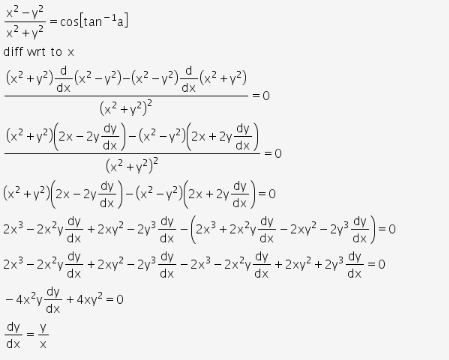 | |
 |  |  |
「(x^2+y^2)*sin(1/sqrt(x^2+y^2))」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 | ||
 |  |  |
「(x^2+y^2)*sin(1/sqrt(x^2+y^2))」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | 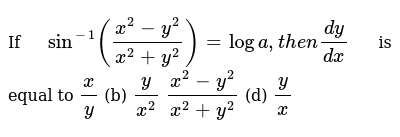 |
 |  | |
 |  |  |
「(x^2+y^2)*sin(1/sqrt(x^2+y^2))」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 | ||
 |  |  |
「(x^2+y^2)*sin(1/sqrt(x^2+y^2))」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 |  | 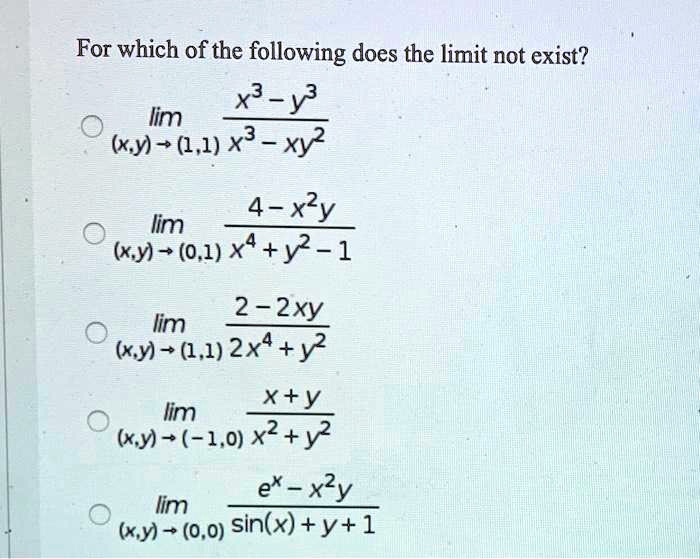 |
 | ||
「(x^2+y^2)*sin(1/sqrt(x^2+y^2))」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 | ||
 |  | |
「(x^2+y^2)*sin(1/sqrt(x^2+y^2))」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 | ||
 |  | |
 |  |  |
「(x^2+y^2)*sin(1/sqrt(x^2+y^2))」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
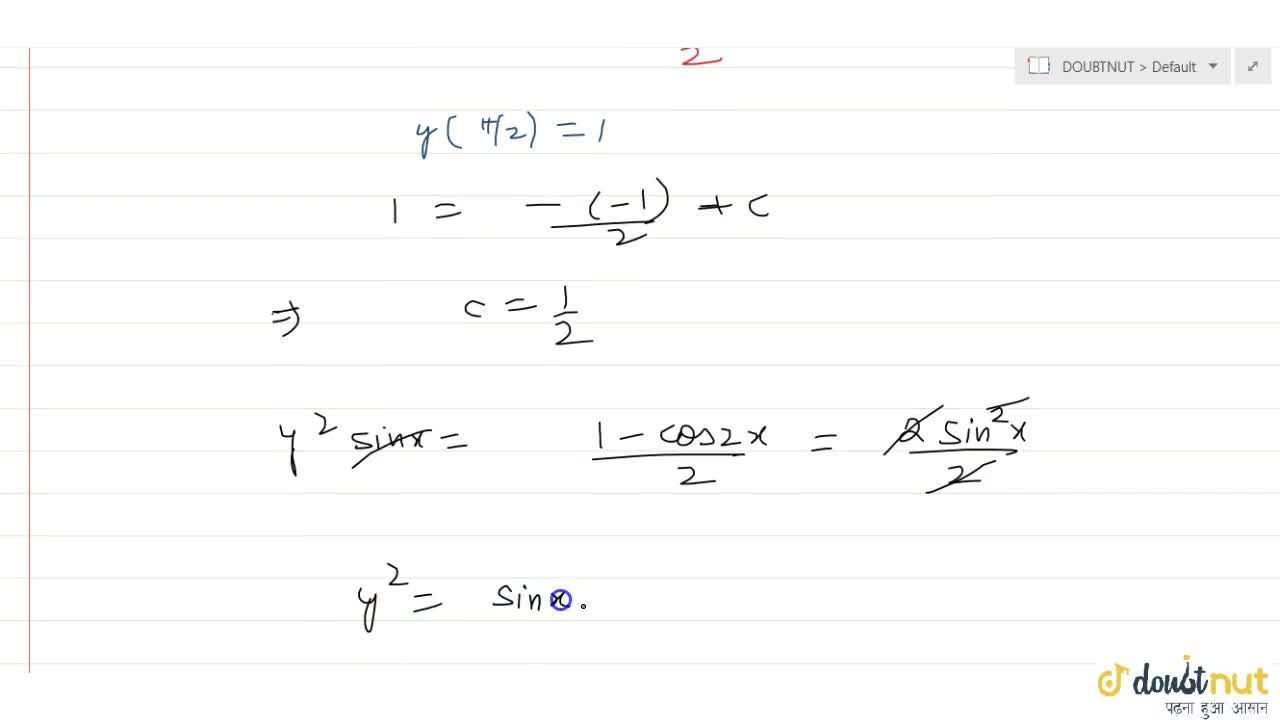 |
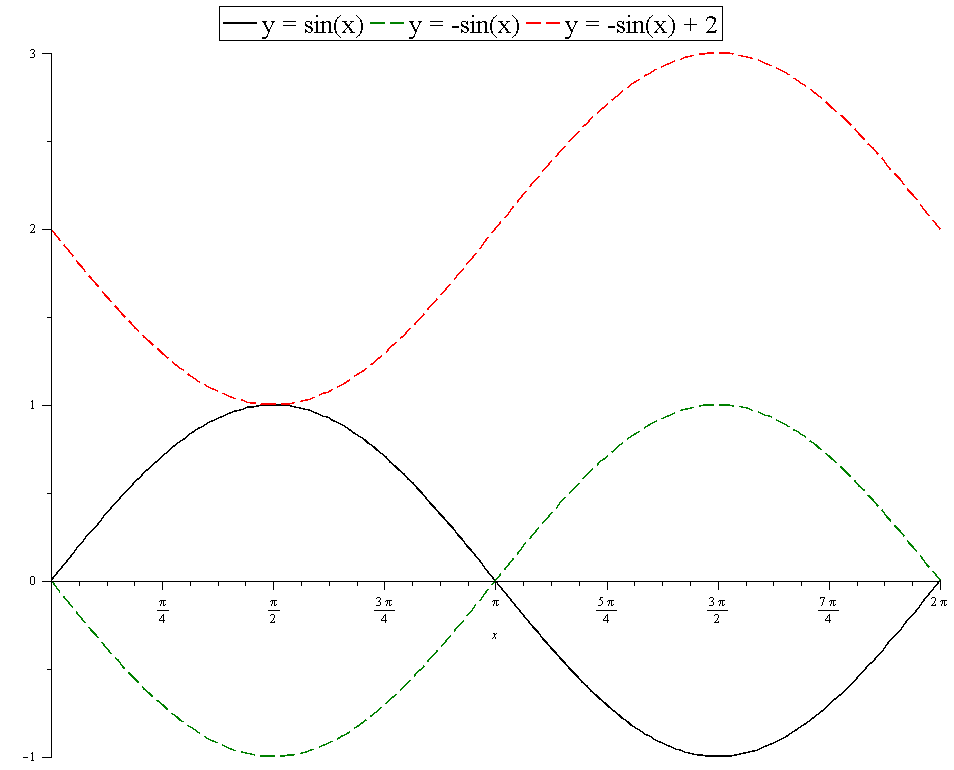
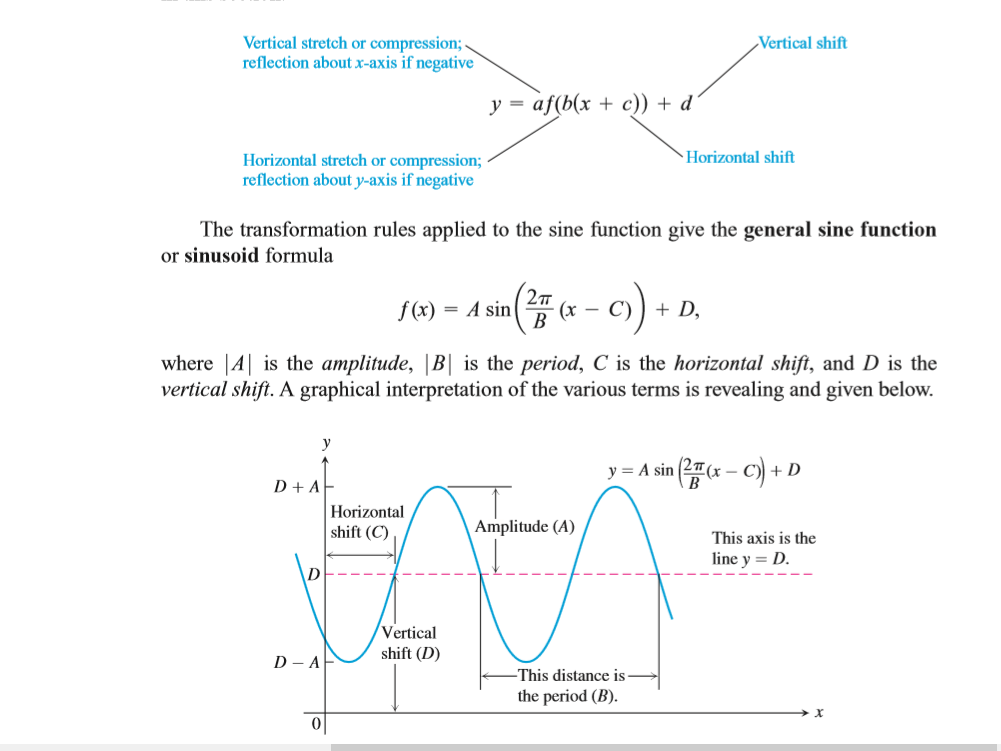
2 ey ey ye) 2 e x = sinh(x)cosh(y) sinh(y) cosh(x) sinh(y) sinh(y) = sinh(x) cosh(y) sinh2 (y) cosh(x) sinh(y) sinh2 (y) = sinh(x) cosh(y) cosh(x) sinh(y) In order to get the corresponding identity for sinh(x y) we can use the even and odd properties of these functions Thus sinh(x y) = sinh(x) cosh (y)cosh(x) sinh( y) = sinh(xGraph y=sin (x/2) y = sin( x 2) y = sin ( x 2) Use the form asin(bx−c) d a sin ( b x c) d to find the variables used to find the amplitude, period, phase shift, and vertical shift a = 1 a = 1 b = 1 2 b = 1 2 c = 0 c = 0 d = 0 d = 0 Find the amplitude a a Amplitude 1 1
Incoming Term: sin(x^2+y^2)/(x^2+y^2) limit, sin(x^2+y^2)/(x^2+y^2), sin^-1(x^2-y^2/x^2+y^2), sin^-1(x^2-y^2/x^2+y^2)=c, if sin^-1(x^2-y^2/x^2+y^2), if sin theta=(x^(2)-y^(2))/(x^(2)+y^(2)) then cos theta=, if sin^-1(x^2-y^2/x^2+y^2)=k, (x^2+y^2)*sin(1/sqrt(x^2+y^2)), cos^-1(x^2-y^2/x^2+y^2)=sin^-1a, f(x y)=(x^2+y^2)sin(1/(x^2+y^2)),




0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿